Fighting Censorship
Aravinth Manivannan | @realaravinthbatsense.net
Evolution of Censorship Cirbumvention Technologies
- VPN
- Tor
- Distributed Web(dWeb)
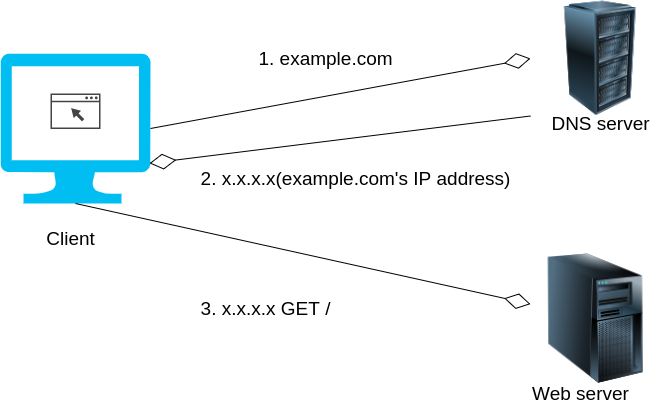
What happens when you normally browse the web?
Workflow
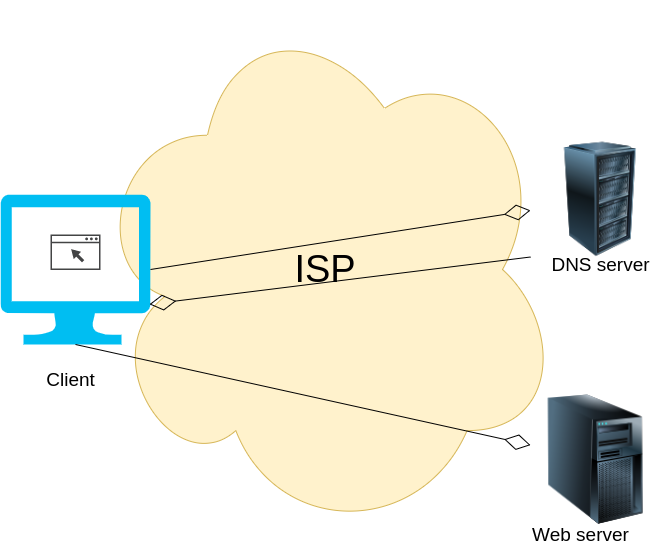
Problems with this workflow
Metadata
What is it?
Metadata (or "data about data") is data that describes a piece of information, apart from the information itself.What does it look like?
➜ guard git:(master) stat DEVELOPMENT.md
File: DEVELOPMENT.md
Size: 2631 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: 10304h/66308d Inode: 28196546 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 1000/aravinth) Gid: ( 1000/aravinth)
Access: 2021-04-15 10:52:23.016926774 +0530
Modify: 2021-04-11 14:07:33.394090235 +0530
Change: 2021-04-11 14:07:33.394090235 +0530
Birth: 2021-04-11 14:07:33.394090235 +0530
Why does it matter?

We kill people based on metadata
- David Cole, Former Director of NSA and CIA
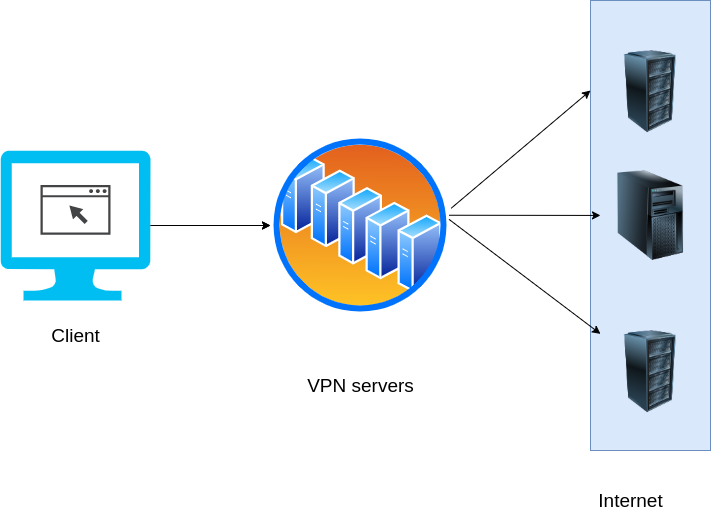
What happens when you use VPN?
Workflow
Pros
- Payload is encrypted
- As far as attacker is concerned, user is accessing VPN server only
Traffic Analysis on a live VPN
Cons
- Too much trust on single entity
- Evil service provider; no way of knowing
- Security breach has cascading effects
- Easy fingerprinting
Tor
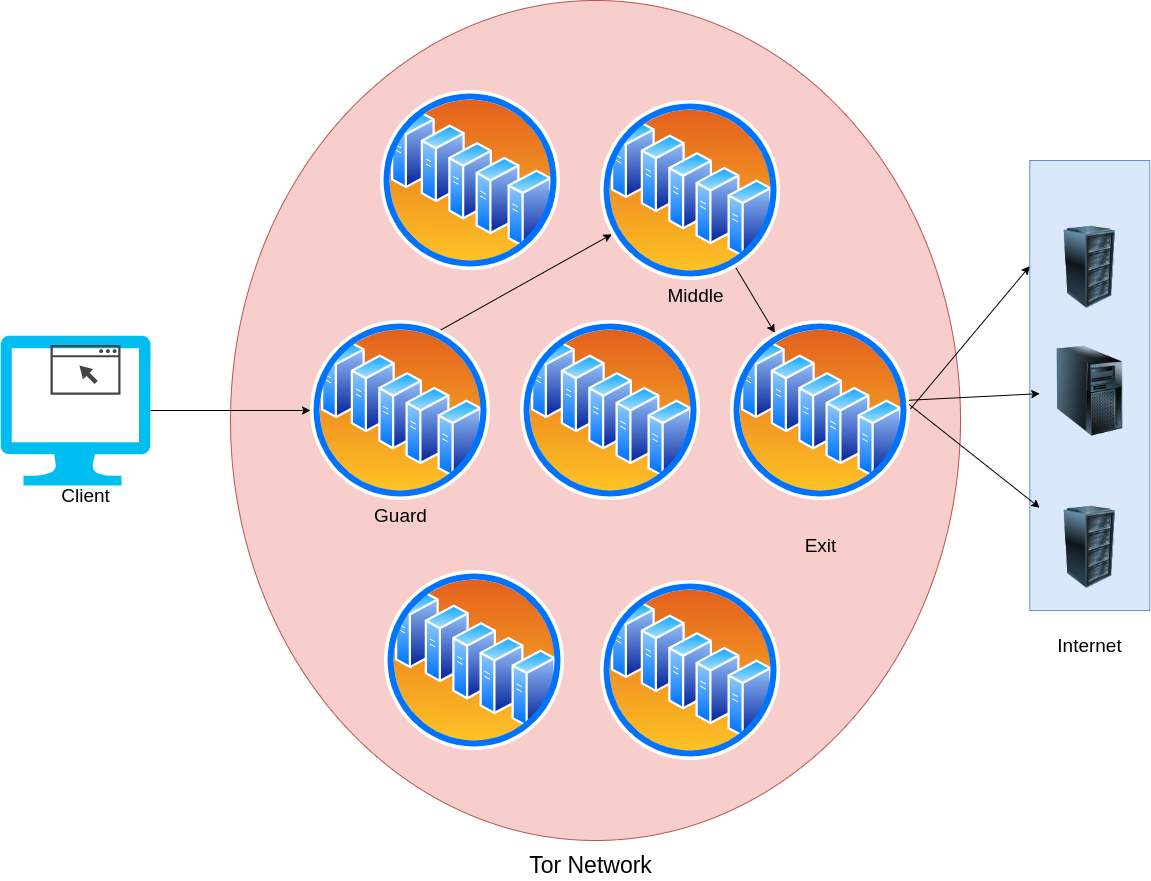
Terminology
- Tor circuit: Single user session
- Relay: A server on the Tor network
- Guard relay: Entry point where client connects to
- Middle relay: Relay between Guard and Exit relays
- Exit relay: Relay that connects to the internet
Data Workflow
Encryption Workflow
Eguard(Emiddle(Eexit(Data)))
- Guard relay: Knows client's IP address
- Middle relay: Doesn't know anything
- Exit relay: Can read user data and user destination
Pros
- Run by the community
- Payload is encrypted thrice
- No single point of failure like VPNs
- Relays are chosen at random
Cons
- Doesn't scale: Every user uses atleast three relays in a session
- Tracking still possible
Attacks on Tor
Traffic Analysis on a live Relay
God's Eye View

What goes in must come out
Denial of Service Attacks
AIM: Find user's source and destination IP addresses- Run a bunch of Guard and Exit relays
- Take down known Exit relays by DoS
-
See if payload size on Exit is same as payload size on Guard:
- Yes: source and destination is mapped
- No: repeat process until sucessful